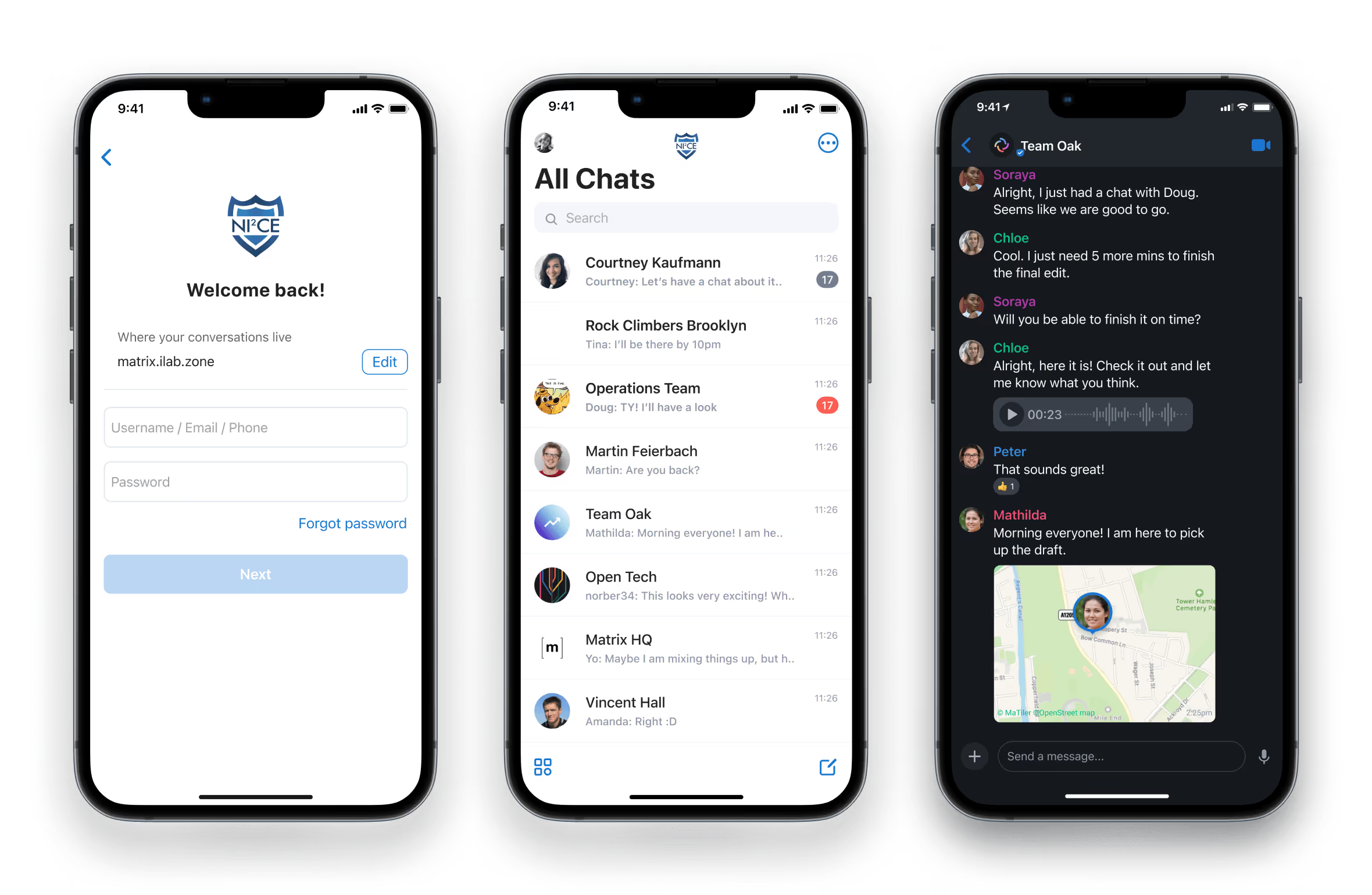
NATO is innovating with a self-hosted open source and cross-platform instant messaging and voice-over-IP service to support digitally sovereign and secure communications.
The experimental project is led by the Allied Command Transformation’s (ACT)
Innovation Hub
. The aim is to complement existing NATO communication solutions with a secure Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) style messenger for ‘unclassified’ use.
The system is called
NI2CE
, which stands for NATO Interoperable Instant Communication Environment.